2022.11.23 20일차 Vector클래스, 추상화클래스
2022. 11. 23. 17:08ㆍJAVA
Vector 클래스
자바의 배열은 고정 길이를 사용함. 즉, 배열이 한번생성되면 배열의 길이를 증가하거나 감소할수없다는 단점이 있음.
Vector클래스는 가변길이의 배열이라고 할 수 있음. (Vector는 내부적으로 배열)
즉, Vector클래스는 객체에 대한 참조값을 저장하는 배열이므로 다양한 객체들이 하나의 Vector에 저장될 수 있고
길이도 필요에 따라 증감할 수 있다는 점이 배열과 다른점이다.
.Vector 클래스의 생성자
Vector() : 10개의 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 길이의 객체를 생성한다.
저장공간이 부족한 경우 10개씩 증가한다.
Vector v = new Vector(); //10개 생성, 10개씩 늘어남
System.out.println("생성 : " + v.capacity());
for(i = 0; i < 11; i++)
{
v.add(new int[0]);
}
System.out.println("크기증가 : " +v.capacity());출력

Vector(int size) : size 개의 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 길이의 객체를 생성한다.
저장공간이 부족할 경우 size개씩 증가한다.
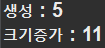
Vector v2 = new Vector(5); //5개 생성, 5개씩 늘어남
System.out.println("생성 : " +v2.capacity());
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
{
v2.add(new int[1]);
}
System.out.println("크기증가 : " +v2.capacity());출력
Vector(int size, int incr) : size 개의 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 길이의 객체를 생성한다
저장공간이 부족할 경우 incr개 만큼 증가한다.
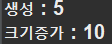
Vector v3 = new Vector(5,3); //5개 생성, 3개씩 늘어남
System.out.println("생성 : " +v3.capacity());
for(i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
v3.add(new int[1]);
}
System.out.println("크기증가 : " +v3.capacity());출력
Vector클래스의 주요 메서드
boolean add(Obejct o) : Vector에 객체를 추가한다.
추가에 성공하면 결과값으로 true, 실패하면 false를 반환한다.
boolean remove(Obejct o) : Vector에 저장되어있는 객체를 제거한다.
제거에 성공하면 true, 실패하면 false를 반환한다.
boolean isEmpty(Obejct o) : Vector가 비어 있는지 검사한다.
비어있으면 true, 비어있지 않으면 false를 반환한다.
Object get(int index) : 지정된위치(index)의 객체를 반환한다.
반환타입이 Object타입이므로 적절한 타입으로의 형변환이 필요하다.
int size() : Vector에 저장된 객체의 개수를 반환한다.
int capacity() : Vector의 크기를 반환한다.
예제)
import java.util.Vector;
class Buyer3
{
int money = 1000;
int bonusPoint = 0;
Vector item = new Vector(); // Vector배열 생성
void buy(Product3 p)
{
if(money < p.price)
{
System.out.println("잔액부족");
return;
}
money -= p.price;
bonusPoint += p.bonusPoint;
item.add(p); // p 객체를 Vector 배열에 추가한다
System.out.println(p + "을(를)구매 하셨습니다.");
}
void refund(Product3 p)
{
if(item.remove(p)) // p와 같은객체가 Vector배열에 있으면 제거하고 true리턴
{
money += p.price;
bonusPoint -= p.bonusPoint;
System.out.println(p + "을(를) 반품 했습니다.");
}
else
{
System.out.println("반품할 물건이 없습니다.");
}
}
void summary()
{
int sum = 0;
String itemList = " ";
int i;
Product3 p = null;
if(item.isEmpty()) //Vector 배열이 비어있으면 true
{
System.out.println("구입한 물건이 없습니다.");
return;
}
for(i = 0; i < item.size(); i++)
{
p = (Product3)item.get(i); //Vector배열에 인덱스 i번째에 있는 객체 Obejct 를 가져온다
sum += p.price;
itemList += (i == 0) ? "" + p : ", " + p;
}
System.out.println("구입한 총 금액 " + sum + "만원 입니다,");
System.out.println("현재 보너스점수 : " + bonusPoint);
System.out.println("구입한 물품은 " + itemList + " 입니다.");
}
}
public class MySample1123_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Buyer3 b = new Buyer3();
Tv4 t = new Tv4();
Computer3 com = new Computer3();
Audio audio = new Audio();
b.summary();
b.buy(t);
b.buy(com);
b.buy(audio);
b.summary();
System.out.println();
b.refund(com);
b.summary();
b.refund(com);
}
}출력

추상클래스
하나 이상의 추상 메소드를 포함하는 클래스를 의미함
추상 메소드: 자식클래스에서 반드시 오버라이딩 해야만 사용할 수 있는 메소드
반드시 사용되어야 하는 메소드를 추상 클래스에 추상 메소드로 선언을 하면,
이 클래스를 상속받는 모든 클래스에서는 이 추상 클래스를 반드시 재정의 해야함
abstract class 클래스이름{
....
abstract 반환타입 메소드이름();
....
}
추상 클래스는 추상 메소드를 포함하고 있다는 점 이외에는 일반 클래스와 모든점이 같다.
즉 생성자와 변수, 일반 메소드도 포함할 수 있음.
예제)
//추상클래스 정의
public abstract class Animal {
//동물이름
protected String name;
public Animal(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
//어떻게 우는지
public abstract String getCry();
//어떻게 움직이는지
public abstract String getMove();
//무엇을 먹는지
public abstract String getFood();
//출력
public abstract void print();
}//상속클래스1
public class Dog extends Animal
{
//울음소리
private String cry;
//이동방법
private String move;
//먹는것
private String food;
//특성
private String dogSp;
public Dog(String name)
{
this(name, "멍멍", "걸어다닌다", "개껌","말 잘드뤄");
}
public Dog(String name, String cry, String move, String food, String dogSp)
{
super(name);
setCry(cry);
setMove(move);
setFood(food);
setDogsp(dogSp);
}
public String getCry()
{
return cry;
}
public void setCry(String cry)
{
this.cry = cry;
}
public String getMove()
{
return move;
}
public void setMove(String move)
{
this.move = move;
}
public String getFood()
{
return food;
}
public void setFood(String food)
{
this.food = food;
}
public String getDogsp()
{
return dogSp;
}
public void setDogsp(String dogSp)
{
this.dogSp = dogSp;
}
public void print()
{
System.out.println("Dog [name : " + getName() + ", cry : " + getCry() + ", move : " + getMove() + ", food : " + getFood() + ", 특성 : " + getDogsp() + "]");
}
}//상속클래스2
public class Cat extends Animal {
//울음소리
private String cry;
//이동방법
private String move;
//먹는것
private String food;
//특성
private String catSp;
public Cat(String name)
{
this(name, "야옹", "걸어다닌다", "츄르", "말 안드뤄");
}
public Cat(String name, String cry, String move, String food, String catSp)
{
super(name);
setCry(cry);
setMove(move);
setFood(food);
setCatsp(catSp);
}
public String getCry()
{
return cry;
}
public void setCry(String cry)
{
this.cry = cry;
}
public String getMove()
{
return move;
}
public void setMove(String move)
{
this.move = move;
}
public String getFood()
{
return food;
}
public void setFood(String food)
{
this.food = food;
}
public String getCatsp()
{
return catSp;
}
public void setCatsp(String catSp)
{
this.catSp = catSp;
}
public void print()
{
System.out.println("Cat [name : " + getName() + ", cry : " + getCry() + ", move : " + getMove() + ", food : " + getFood() + ", 특성 : " + getCatsp() + "]");
}
}//상속클래스3
public class Bird extends Animal{
//울음소리
private String cry;
//이동방법
private String move;
//먹는것
private String food;
//특성
private String birdSp;
public Bird(String name)
{
this(name, "쨱쨱", "날아다닌다", "씨앗","날개가 있음");
}
public Bird(String name, String cry, String move, String food, String birdSp)
{
super(name);
setCry(cry);
setMove(move);
setFood(food);
setBirdsp(birdSp);
}
public String getCry()
{
return cry;
}
public void setCry(String cry)
{
this.cry = cry;
}
public String getMove()
{
return move;
}
public void setMove(String move)
{
this.move = move;
}
public String getFood()
{
return food;
}
public void setFood(String food)
{
this.food = food;
}
public String getBirdsp()
{
return birdSp;
}
public void setBirdsp(String birdSp)
{
this.birdSp = birdSp;
}
public void print()
{
System.out.println("Brid [name : " + getName() + ", cry : " + getCry() + ", move : " + getMove() + ", food : " + getFood() + ", 특성 : " + getBirdsp() + "]");
}
}//메인클래스 정의
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog("개");
Cat cat = new Cat("고양이");
Bird bird = new Bird("새");
dog.print();
cat.print();
bird.print();
dog.setMove("껑충껑충");
cat.setFood("생선");
bird.setCry("삐약삐약");
System.out.println();
dog.print();
cat.print();
bird.print();
}
}출력

'JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 2022.11.25 JAVA 22일차 예외처리(try ~ catch ~ finally) (0) | 2022.11.25 |
|---|---|
| 2022.11.24 JAVA 21일차 인터페이스 (0) | 2022.11.24 |
| 2022.11.22 JAVA 19일차 다형성 (0) | 2022.11.22 |
| 2022.11.21 JAVA 18일차 오버라이딩, 접근제어자 (0) | 2022.11.22 |
| 2022.11.18 JAVA 17일차 객체지향 응용문제(상수) (0) | 2022.11.22 |